Abstract
Objective
This study aimed at analyzing results of surgery for lung cancer in relation to hospital volume to see if a straightforward relation exists between hospital volume and surgical outcome.
Methods
Two data sets collected nationwide in Japan were retrospectively studied by statistical analysis: 18 055 patients operated on during an average year for the most recent 4 years for an analysis of hospital mortality and 3233 patients operated on duraing 1989 for analysis of the 5-year survival rate. First, we examined the correlations of hospital volume with each outcome, which was estimated using the empirical Bayes (EB) method to stabilize any large variation due to the small sample. Then we estimated the volume effects using generalized regression models. Perioperative mortality and the 5-year survival rate in relation to hospital volume were measured.
Results
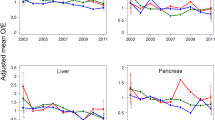
No statistically significant correlations between hospital volume and each outcome have been shown (EB mortality 1.51%, P = 0.0566; 5-year survival 48.9%, P = 0.333). Regarding the volume effect, only the lowest-volume subgroup showed a statistically significant higher perioperative mortality rate and a lower 5-year survival rate compared to the highest-volume counterpart, but many hospitals of the lowest-volume subgroup had operated on more patients with advanced-stage disease.
Conclusions
No straightforward correlation was seen between hospital volume and surgical outcome. Hospital volume may not be a suitable single tool to predict the outcome of lung cancer surgery. We should reserve the conclusion that low-volume hospitals offer less effective surgery. We need a risk-adjusted database to study this topic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
EL Hannan M Radzyner SuffixJr D Rubin J Dougherty MF Brennan (2002) ArticleTitleThe influence of hospital and surgeon volume on in-hospital mortality for colectomy, gastrectomy, and lung lobectomy in patients with cancer Surgery 131 6–15 Occurrence Handle10.1067/msy.2002.120238 Occurrence Handle11812957
PB Bach LD Cramer D Schrag RJ Downey SE Gelfand CB Begg (2001) ArticleTitleThe influence of hospital volume on survival after resection for lung cancer N Engl J Med 345 181–8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mvht12jsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM200107193450306 Occurrence Handle11463014
T Treasure M Utley A Bailey (2003) ArticleTitleAssessment of whether in-hospital mortality for lobectomy is a useful standard for the quality of lung cancer surgery: retrospective study BMJ 327 73–5 Occurrence Handle10.1136/bmj.327.7406.73 Occurrence Handle12855523 Occurrence Handle164918
Shirakusa T, Sohara Y, Hata E, Funatsu T, Maeda M, Matsuura Y, et al. 1994 Report on survival rate after surgery for lung cancer by the Science Committee. J Jpn Assoc Chest Surg 1996;10 (originally unpaged)
D Clayton J Kaldor (1987) ArticleTitleEmpirical Bayes estimates of age-standardized relative risks for use in disease mapping Biometrics 43 671–82 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c%2FisFektA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.2307/2532003 Occurrence Handle3663823
KY Liang SL Zeger (1986) ArticleTitleLongitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models Biometrika 73 13–22 Occurrence Handle10.1093/biomet/73.1.13
GA Silvestri J Handy D Lackland E Corley CE Reed (1998) ArticleTitleSpecialists achieve better outcomes than generalists for lung cancer surgery Chest 114 675–80 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvhsVSrsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1378/chest.114.3.675 Occurrence Handle9743149
RAM Damhuis PR Schuette (1996) ArticleTitleResection rates and postoperative mortality in 7899 patients with lung cancer Eur Respir J 9 7–10 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28vjtFantg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1183/09031936.96.09010007 Occurrence Handle8834326
EVA Finlayson JD Birkmeyer (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of hospital volume on life expectancy after selected cancer operations in older adults: a decision analysis J Am Coll Surg 196 410–7 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1072-7515(02)01753-2 Occurrence Handle12648693
WA Fry HR Menck DP Winchester (1996) ArticleTitleThe national cancer data base report on lung cancer Cancer 77 1947–55 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK283gvVGqtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960501)77:9<1947::AID-CNCR27>3.0.CO;2-Z Occurrence Handle8646697
AE Martin-Ucar DA Waller JL Atkins D Swinson KJ O'Byrne MD Peake (2004) ArticleTitleThe beneficial effects of specialist thoracic surgery on the resection rate for non-small-cell lung cancer Lung Cancer 46 227–32 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.03.010 Occurrence Handle15474671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osada, H., Yamakoshi, E. Hospital volume and surgical outcomes of lung cancer in Japan. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 55, 360–365 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-007-0114-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-007-0114-x