Abstract
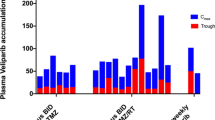
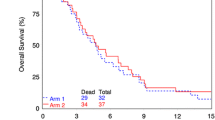
We conducted a phase I trial to examine the maximally tolerated dose (MTD) of the oral protease inhibitor nelfinavir (NFV) in combination with temozolomide and concurrent radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma and to gather preliminary data for response. The study was conducted in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma after surgical resection. Patients were treated with standard radiotherapy (6,000 cGy to the gross tumor volume), temozolomide (75 mg/m2 daily) together with daily oral NFV starting 7–10 days prior to chemoradiotherapy continuing for the duration of chemoradiation for 6 weeks. Temozolomide (150–200 mg/m2) was resumed 4 weeks after completion of chemoradiotherapy. Two dose levels of NFV were investigated: 625 mg twice daily (bid) and 1,250 mg bid in a cohort escalation design. A total of 21 patients were enrolled. At the maximum tolerated dose, 18 subjects were enrolled to further evaluate toxicity and for preliminary estimate of efficacy for further phase II study. No dose-limiting toxicity was noted at 625 mg bid. At 1,250 mg bid, 3 dose-limiting episodes of hepatotoxicity were noted and one dose-limiting episode of diarrhea. The MTD for this study was 1,250 mg bid. NFV (1,250 mg bid) concurrent with temozolomide and radiotherapy is tolerated in most patients with glioblastoma. At the 1,250 mg bid dose level, patients should be monitored for hepatotoxicity and GI side effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Nishikawa R, Sugiyama T, Narita Y, Fumari F, Cavenee WK, Matsutani M (2004) Immunohistochemical analysis of the mutant epidermal growth factor, deltaEGFR, in glioblastoma. Brain Tumor Pathol 21(2):53–56
Moldvay J, Scheid P, Wild P, Nabil K, Siat J, Borrelly J et al (2000) Predictive survival markers in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 6(3):1125–1134
Schneider PM, Praeuer HW, Stoeltzing O, Boehm J, Manning J, Metzger R, Fink U, Wegerer S, Hoelscher AH, Roth JA (2000) Multiple molecular marker testing (p53, C-Ki-ras, c-erbB-2) improves estimation of prognosis in potentially curative resected non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 83(4):473–479
Harari PM, Huang SM (2001) Head and neck cancer as a clinical model for molecular targeting of therapy: combining EGFR blockade with radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49(2):427–433
McKenna WG, Weiss MC, Endlich B, Ling CC, Bakanauskas VJ, Kelsten ML, Muschel RJ (1990) Synergistic effect of the v-myc oncogene with H-ras on radioresistance. Cancer Res 50(1):97–102
Bernhard EJ, Stanbridge EJ, Gupta S, Gupta AK, Soto D, Bakanauskas VJ, Cerniglia GJ, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG (2000) Direct evidence for the contribution of activated N-ras and Kras oncogenes to increased intrinsic radiation resistance in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 60(23):6597–6600
Gupta AK, Bakanauskas VJ, Cerniglia GJ, Cheng Y, Bernhard EJ, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG (2001) The Ras radiation resistance pathway. Cancer Res 61(10):4278–4282
Gupta AK, McKenna WG, Weber CN, Feldman MD, Goldsmith JD, Mick R, Machtay M et al (2002) Local recurrence in head and neck cancer: relationship to radiation resistance and signal transduction. Clin Cancer Res 8(3):885–892
Gupta AK, Cerniglia GJ, Mick R, Ahmed MS, Bakanauskas VJ, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG (2003) Radiation sensitization of human cancer cells in vivo by inhibiting the activity of PI3K using LY294002. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56(3):846–853
Grana TM, Rusyn EV, Zhou H, Sartor CI, Cox AD (2002) Ras mediates radioresistance through both phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and Raf-dependent but mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase-independent signaling pathways. Cancer Res 62(14):4142–4150
Carr A, Samaras K, Thorisdottir A, Kaufmann GR, Chisholm DJ, Cooper DA (1999) Diagnosis, prediction, and natural course of HIV-1 protease-inhibitor associated lipodystrophy, hyperlipidaemia, and diabetes mellitus: a cohort study. Lancet 353(9170):2093–2099
Powderly WG (2002) Long-term exposure to lifelong therapies. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 29(Suppl 1):S28–S40
Bae SS, Cho H, Mu J, Birnbaum MJ (2003) Isoform-specific regulation of insulin-dependent glucose uptake by Akt/protein kinase B. J Biol Chem 278(49):49530–49536
Cross DA, Watt PW, Shaw M, Downes CP, van der Kaay J, Holder JC, Cohen P (1997) Insulin activates protein kinase B, inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3 and activates glycogen synthase by rapamycin-insensitive pathways in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. FEBS Lett 406(1–2):211–215
Saag MS, Tebas P, Sension M, Conant M, Myers R, Chapman SK, Anderson R (2001) Randomized, double-blind comparison of two nelfinavir doses plus nucleosides in HIV-infected patients (Agouron study 511). AIDS 15(15):1971–1978
Stadler RF, Gregorcyk SG, Euhus DM, Place RJ, Huber PH, Simmang CL (2004) Outcome of HIV-infected patients with invasive squamous-cell carcinoma of the anal canal in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Dis Colon Rectum 47(8):1305–1309
Thomson Healthcare (2004) Physicians' desk reference, 58th edn. Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ
Jiang Z, Pore N, Cerniglia GJ, Mick R, Georgescu M, Bernhard EJ, Hahn SM, Gupta AK, Maity A (2007) Phosphatase and tensin homologue deficiency in glioblastoma confers resistance to radiation and temozolomide that is reversed by the protease inhibitor nelfinavir. Cancer Res 67(9):4467–4473
James JS (1997) Nelfinavir (Viracept) approved: fourth protease inhibitor available. AIDS Treat News 267:1–2
Rodriguez-French A, Boghossian J, Gray GE, Nadler JP, Quinones AR, Sepulveda GE, Millard JM, Wannamaker PG (2004) The NEAT study: a 48-week open-label study to compare the antiviral efficacy and safety of GW433908 versus nelfinavir in antiretroviral therapy—naïve HIV-1-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 35(1):22–32
Chang EL, Akyurek S, Avalos T, Rebueno N, Spicer C, Garcia J, Famiglietti R et al (2007) Evaluation of peritumoral edema in the delineation of radiotherapy clinical target volumes for glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68(1):144–150
Milano MT, Okunieff P, Donatello RS, Mohile NA, Sul J, Walter KA, Korones DN (2010) Patterns and timing of recurrence after temozolomide-based chemoradiation for glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(3):1147–1155
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Pennsylvania, ASCO Young Investigator Award, Burroughs Wellcome Career Award for Medical Scientists (1006792) and the National Institute of Health/National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke (K08 NS076548-01). We acknowledge the Department of Radiation Oncology Clinical Research Coordinators for their assistance with the study. The clinical trial protocol was formulated and written at the ASCO/AACR: Methods in Clinical Cancer Research (Vail) Workshop.
Conflict of interest
The University of Pennsylvania has a patent pending on the use of compounds of the type like NFV in combination with radiation. Under the policies of the University of Pennsylvania, the University may receive financial benefits based on the results of this study. There are no conflicts of interest to disclose for any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Michelle Alonso-Basanta and Penny Fang have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alonso-Basanta, M., Fang, P., Maity, A. et al. A phase I study of nelfinavir concurrent with temozolomide and radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 116, 365–372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1303-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1303-3